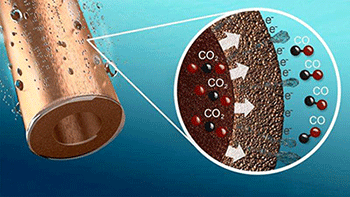
An important innovation is the optimized interface between gas, fluid and copper particles, allowing the very efficient supply of CO2 and removal of the product, CO.
Image: University of Twente
In an effort to convert carbon dioxide into carbon dioxide, researchers have developed an electrode in the form of a hollow porous coper fiber that completes this transformation at an extremely efficient level.
The researchers, including ECS member Marc T.M. Koper, believe that this development could give the industrial industry an edge, where it would be extremely beneficial for chemical processes that require gas conversion.
(MORE: Read additional research by Koper.)
The process is not confined to the conversion of carbon dioxide to carbon monoxide, however. Because the manufacturing method is suited for other fibers, it could also be applied to the conversion of oxygen in a fuel cell or hydrogen conversion in the electrochemical production of ammonia.
While the principal idea behind the process is straightforward, the efficiency and selectivity of the reaction is the surprising factor.