 Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy (2nd Edition), by Mark E. Orazem and Bernard Tribollet, provides the fundamentals needed to apply impedance spectroscopy to a broad range of applications with emphasis on obtaining physically meaningful insights from measurements. The second edition provides expanded treatment of the influence of mass transport, time-constant dispersion, kinetics, and constant-phase elements.
Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy (2nd Edition), by Mark E. Orazem and Bernard Tribollet, provides the fundamentals needed to apply impedance spectroscopy to a broad range of applications with emphasis on obtaining physically meaningful insights from measurements. The second edition provides expanded treatment of the influence of mass transport, time-constant dispersion, kinetics, and constant-phase elements.
The new edition improves on the clarity of some of the chapters, more than doubling the number of examples. It has more in-depth treatment of background material needed to understand impedance spectroscopy, including electrochemistry, complex variables, and differential equations. This title includes expanded treatment of the influence of mass transport and kinetics, and reflects recent advances in the understanding of frequency dispersion and interpretation of constant-phase elements.
This monograph is sponsored by ECS, and published by John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
About the Authors
Mark E. Orazem is a Professor of Chemical Engineering at the University of Florida. He organized the 6th International Symposium on Electrochemical Impedence Spectroscopy and teaches a short course on impedance spectroscopy for The Electrochemical Society.
Bernard Tribollet is the Director of Research at the Centre National de la Recherche Scientifique and Associate Director of the Laboratoire Interfaces et Systémes Electrochemique at Pierre and Marie Curie University. Dr. Tribollet instructs an annual short course on impedance spectroscopy.
Visit the ECS Online Store to purchase your copy today!
 A new issue of ECS Transactions (ECST) has just been published. This issue incorporates 333 papers from the upcoming 15th International Symposium on Solid Oxide Fuel Cells (SOFC-XV). This conference will be held in Hollywood, Florida, USA, July 23-28, 2017.
A new issue of ECS Transactions (ECST) has just been published. This issue incorporates 333 papers from the upcoming 15th International Symposium on Solid Oxide Fuel Cells (SOFC-XV). This conference will be held in Hollywood, Florida, USA, July 23-28, 2017.

 On June 21, publishing giant Elsevier won a legal judgement against websites like Sci-Hub, which illicitly offer access to over 60 million academic articles. The court ruled in Elsevier’s favor, awarding the publisher $15 million in damages for copyright infringement.
On June 21, publishing giant Elsevier won a legal judgement against websites like Sci-Hub, which illicitly offer access to over 60 million academic articles. The court ruled in Elsevier’s favor, awarding the publisher $15 million in damages for copyright infringement. Sci-Hub launched a few years back when Alexandra Elbakyan of Kazakhstan was struggling to find affordable and relevant research through her institution. Fast forward to 2017 and Sci-Hub serves as one of the most common sites that seeks to circumvent paywalls and provide access to scholarly literature.
Sci-Hub launched a few years back when Alexandra Elbakyan of Kazakhstan was struggling to find affordable and relevant research through her institution. Fast forward to 2017 and Sci-Hub serves as one of the most common sites that seeks to circumvent paywalls and provide access to scholarly literature. Recently there has been a spate of comment expressing frustration about the allegedly slow progress of open access, and especially Green open access. It is hard to disagree with some of this sentiment, but it is important that frustration not lead us into trying to solve a problem with a worse solution. The key, I believe, to making real advances in open access is to walk away from the commercial publishers who have dominated the market for scholarship. Only if we do that can libraries free up money from our collection budgets to do truly new things. A new business model with the same old players, even if it were possible, would be a mistake.
Recently there has been a spate of comment expressing frustration about the allegedly slow progress of open access, and especially Green open access. It is hard to disagree with some of this sentiment, but it is important that frustration not lead us into trying to solve a problem with a worse solution. The key, I believe, to making real advances in open access is to walk away from the commercial publishers who have dominated the market for scholarship. Only if we do that can libraries free up money from our collection budgets to do truly new things. A new business model with the same old players, even if it were possible, would be a mistake.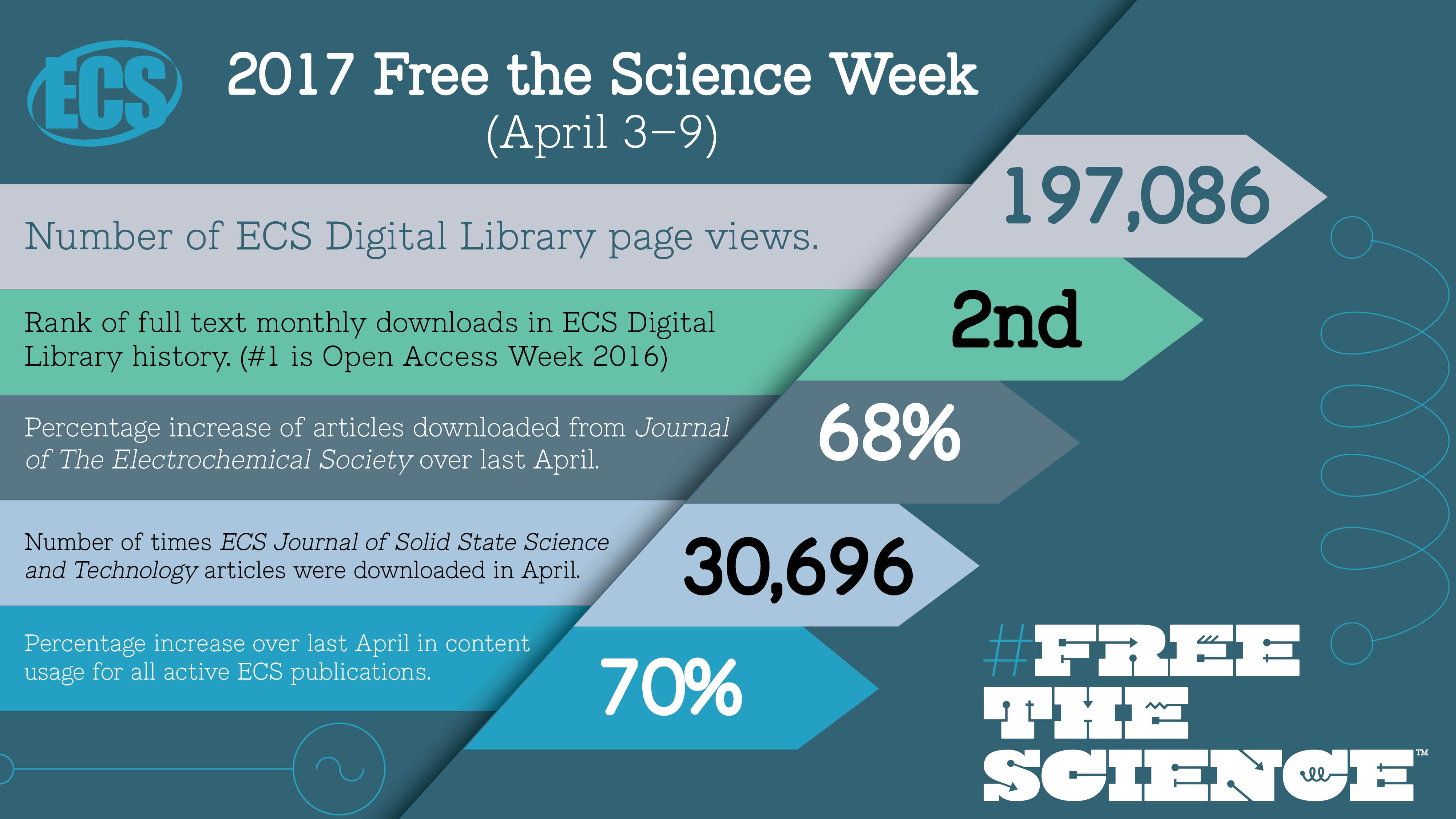
 What is “open science”?
What is “open science”? Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy (2nd Edition), by Mark E. Orazem and Bernard Tribollet, provides the fundamentals needed to apply impedance spectroscopy to a broad range of applications with emphasis on obtaining physically meaningful insights from measurements. The second edition provides expanded treatment of the influence of mass transport, time-constant dispersion, kinetics, and constant-phase elements.
Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy (2nd Edition), by Mark E. Orazem and Bernard Tribollet, provides the fundamentals needed to apply impedance spectroscopy to a broad range of applications with emphasis on obtaining physically meaningful insights from measurements. The second edition provides expanded treatment of the influence of mass transport, time-constant dispersion, kinetics, and constant-phase elements.