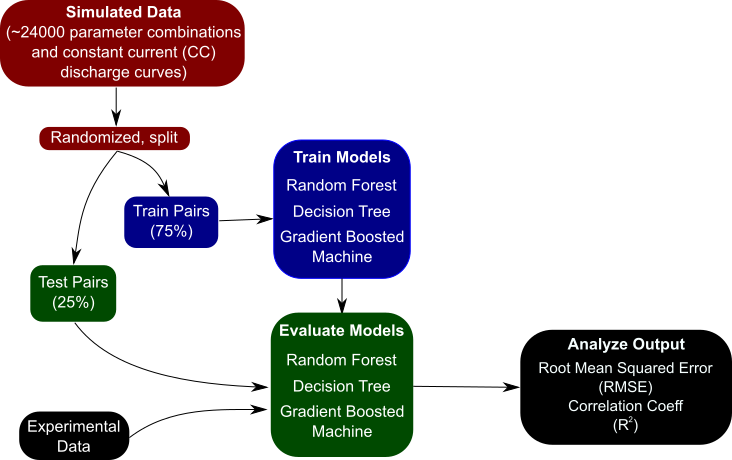
New graphene printing technology can produce electronic circuits that are low-cost, flexible, highly conductive and water repellent, researchers report.
New graphene printing technology can produce electronic circuits that are low-cost, flexible, highly conductive and water repellent, researchers report.
The nanotechnology “would lend enormous value to self-cleaning wearable/washable electronics that are resistant to stains, or ice and biofilm formation,” according to the new paper.
“We’re taking low-cost, inkjet-printed graphene and tuning it with a laser to make functional materials,” says Jonathan Claussen, an assistant professor of mechanical engineering at Iowa State University, an associate of the US Department of Energy’s Ames Laboratory, and the corresponding author of the paper in the journal Nanoscale.


 Join us as ECS and La Sociedad Mexicana de Electroquímica comes together for the
Join us as ECS and La Sociedad Mexicana de Electroquímica comes together for the 
 Editor’s note: On Jan. 22, 2018, the Trump administration announced plans to
Editor’s note: On Jan. 22, 2018, the Trump administration announced plans to 
 The winner of the inaugural
The winner of the inaugural  At each of our biannual meetings, ECS works with our education committee to provide professional development programming to help our students and young professionals develop skills for their current and future careers. ECS provides new topics at each meeting and helps attendees build their professional network.
At each of our biannual meetings, ECS works with our education committee to provide professional development programming to help our students and young professionals develop skills for their current and future careers. ECS provides new topics at each meeting and helps attendees build their professional network.