By: Timothy J. Jorgensen, Georgetown University
 Ask people to name the most famous historical woman of science and their answer will likely be: Madame Marie Curie. Push further and ask what she did, and they might say it was something related to radioactivity. (She actually discovered the radioisotopes radium and polonium.) Some might also know that she was the first woman to win a Nobel Prize. (She actually won two.)
Ask people to name the most famous historical woman of science and their answer will likely be: Madame Marie Curie. Push further and ask what she did, and they might say it was something related to radioactivity. (She actually discovered the radioisotopes radium and polonium.) Some might also know that she was the first woman to win a Nobel Prize. (She actually won two.)
But few will know she was also a major hero of World War I. In fact, a visitor to her Paris laboratory in October of 1917 – 100 years ago this month – would not have found either her or her radium on the premises. Her radium was in hiding and she was at war.
For Curie, the war started in early 1914, as German troops headed toward her hometown of Paris. She knew her scientific research needed to be put on hold. So she gathered her entire stock of radium, put it in a lead-lined container, transported it by train to Bordeaux – 375 miles away from Paris – and left it in a safety deposit box at a local bank. She then returned to Paris, confident that she would reclaim her radium after France had won the war.
With the subject of her life’s work hidden far away, she now needed something else to do. Rather than flee the turmoil, she decided to join in the fight. But just how could a middle-aged woman do that? She decided to redirect her scientific skills toward the war effort; not to make weapons, but to save lives.

 A new sodium-based battery can store the same amount of energy as a state-of-the-art lithium ion at a substantially lower cost.
A new sodium-based battery can store the same amount of energy as a state-of-the-art lithium ion at a substantially lower cost. A new flexible, paper-based supercapacitor could power wearable electronics.
A new flexible, paper-based supercapacitor could power wearable electronics.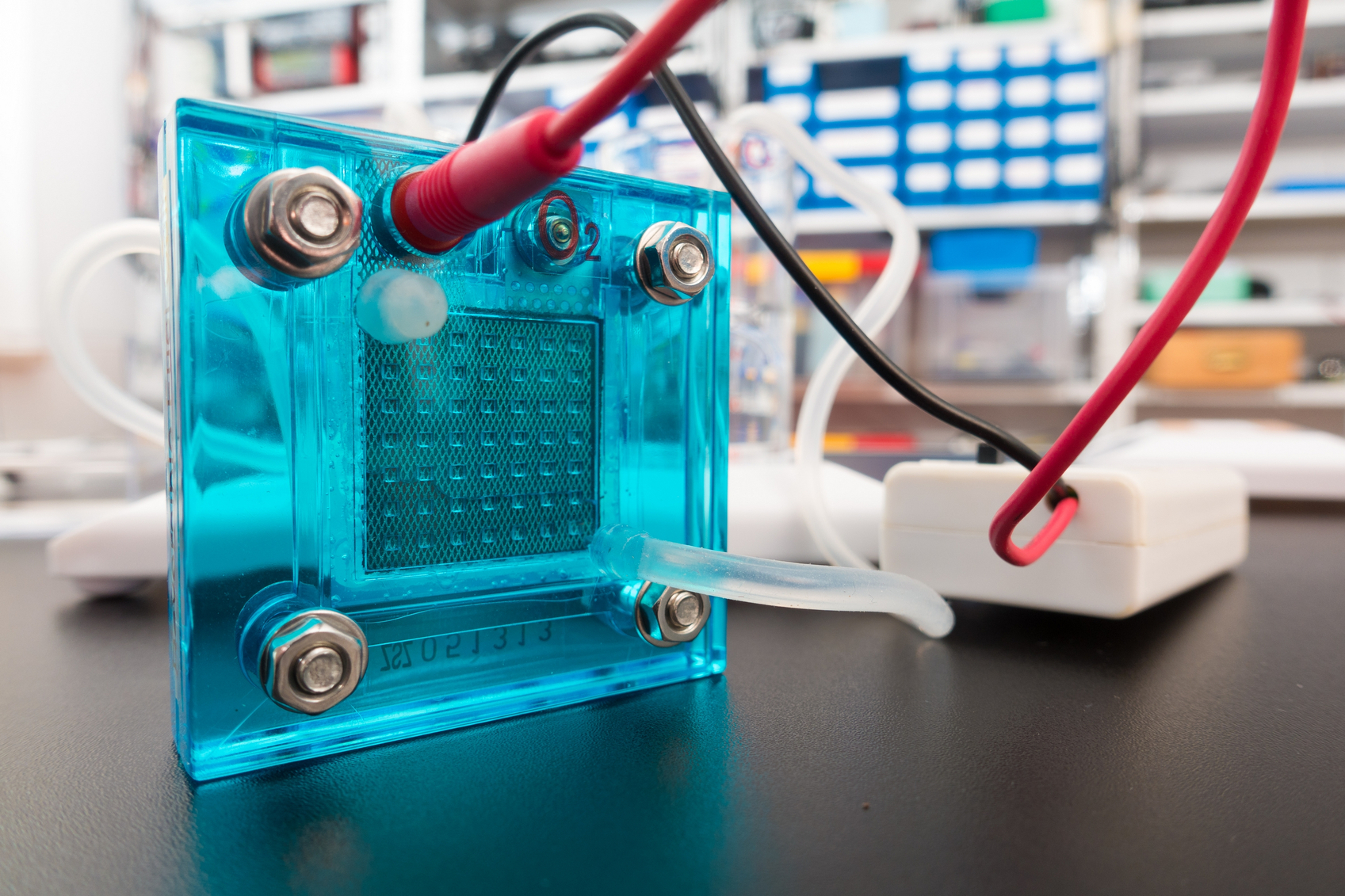 A closer look at catalysts is giving researchers a better sense of how these atom-thick materials produce hydrogen.
A closer look at catalysts is giving researchers a better sense of how these atom-thick materials produce hydrogen. Tech Highlights was prepared by David Enos and Mike Kelly of Sandia National Laboratories, Colm Glynn and David McNulty of University College Cork, Ireland, Zenghe Liu of Verily Life Science, and Donald Pile of Rolled-Ribbon Battery Company. This article was originally published in the
Tech Highlights was prepared by David Enos and Mike Kelly of Sandia National Laboratories, Colm Glynn and David McNulty of University College Cork, Ireland, Zenghe Liu of Verily Life Science, and Donald Pile of Rolled-Ribbon Battery Company. This article was originally published in the  Engineers working to make solar cells more cost effective ended up finding a method for making sonar-like collision avoidance systems in self-driving cars.
Engineers working to make solar cells more cost effective ended up finding a method for making sonar-like collision avoidance systems in self-driving cars.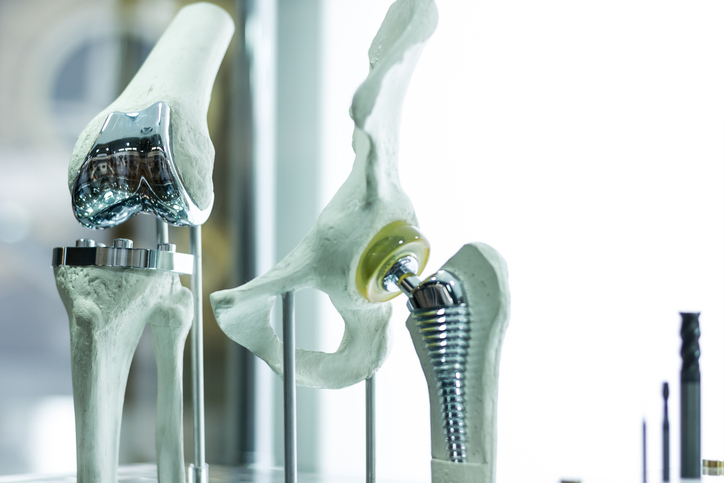 The development of prosthetics has changed many lives, providing mobility options and allowing for more active lives. But all artificial limbs aren’t perfect. Some can be painful, difficult to use, and lead to possible skin infections. The Office of Naval Research is looking to change that, providing new options for those in need of artificial limbs.
The development of prosthetics has changed many lives, providing mobility options and allowing for more active lives. But all artificial limbs aren’t perfect. Some can be painful, difficult to use, and lead to possible skin infections. The Office of Naval Research is looking to change that, providing new options for those in need of artificial limbs. Just a few months ago, business magnate Elon Musk announced that he would spearhead an effort to build the
Just a few months ago, business magnate Elon Musk announced that he would spearhead an effort to build the  Submit your manuscripts to the Journal of The Electrochemical Society (JES)
Submit your manuscripts to the Journal of The Electrochemical Society (JES)