By: Rand Wilcox, University of Southern California – Dornsife College of Letters, Arts and Sciences
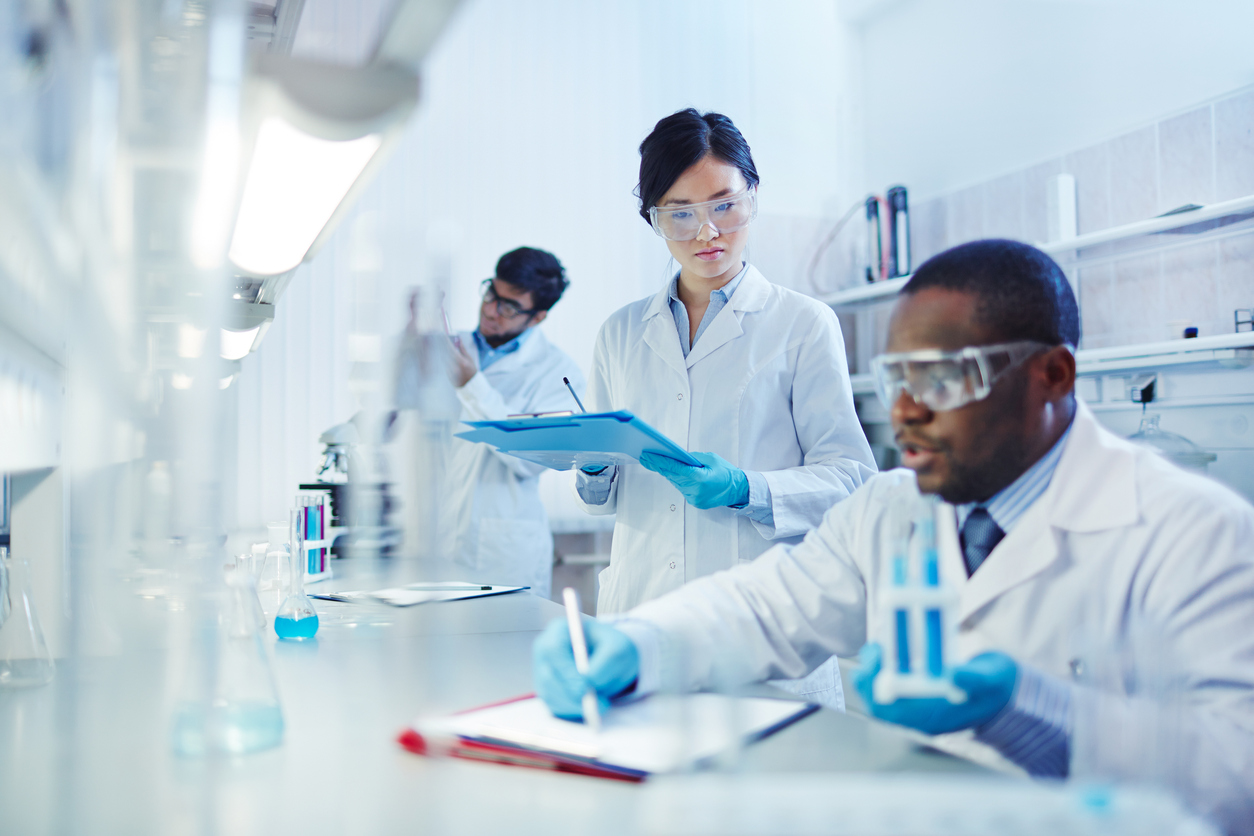 No matter the field, if a researcher is collecting data of any kind, at some point he is going to have to analyze it. And odds are he’ll turn to statistics to figure out what the data can tell him.
No matter the field, if a researcher is collecting data of any kind, at some point he is going to have to analyze it. And odds are he’ll turn to statistics to figure out what the data can tell him. ![]()
A wide range of disciplines – such as the social sciences, marketing, manufacturing, the pharmaceutical industry and physics – try to make inferences about a large population of individuals or things based on a relatively small sample. But many researchers are using antiquated statistical techniques that have a relatively high probability of steering them wrong. And that’s a problem if it means we’re misunderstanding how well a potential new drug works, or the effects of some treatment on a city’s water supply, for instance.
As a statistician who’s been following advances in the field, I know there are vastly improved methods for comparing groups of individuals or things, as well as understanding the association between two or more variables. These modern robust methods offer the opportunity to achieve a more accurate and more nuanced understanding of data. The trouble is that these better techniques have been slow to make inroads within the larger scientific community.


 Lithium-ion batteries power a vast majority of the world’s portable electronics, but the magnification of recent safety incidents have some looking for new ways to keep battery-related hazards at bay. The U.S. Navy is one of those groups, with chemists in the U.S. Naval Research Laboratory (NRL) unveiling a new battery, which they say is both safe and rechargeable for applications such as electric vehicles and ships.
Lithium-ion batteries power a vast majority of the world’s portable electronics, but the magnification of recent safety incidents have some looking for new ways to keep battery-related hazards at bay. The U.S. Navy is one of those groups, with chemists in the U.S. Naval Research Laboratory (NRL) unveiling a new battery, which they say is both safe and rechargeable for applications such as electric vehicles and ships. Submit your manuscripts for the ECS Journal of Solid State Science and Technology (JSS) Focus Issue on
Submit your manuscripts for the ECS Journal of Solid State Science and Technology (JSS) Focus Issue on  Like all things, batteries have a finite lifespan. As batteries get older and efficiency decreases, they enter what researchers call “capacity fade,” which occurs when the amount of charge your battery could once hold begins to decrease with repeated use.
Like all things, batteries have a finite lifespan. As batteries get older and efficiency decreases, they enter what researchers call “capacity fade,” which occurs when the amount of charge your battery could once hold begins to decrease with repeated use. After an unusually intense heat wave, downpour, or drought, Noah Diffenbaugh and his research group inevitably get phone calls and emails asking whether human-caused climate change played a role.
After an unusually intense heat wave, downpour, or drought, Noah Diffenbaugh and his research group inevitably get phone calls and emails asking whether human-caused climate change played a role. Researchers from Columbia University School of Engineering and Applied Science recently developed a method that could result in safer, longer-lasting, bendable lithium-ion batteries. To do this, the team applied ice-templating to control the structure of the solid electrolyte for lithium-ion batteries.
Researchers from Columbia University School of Engineering and Applied Science recently developed a method that could result in safer, longer-lasting, bendable lithium-ion batteries. To do this, the team applied ice-templating to control the structure of the solid electrolyte for lithium-ion batteries. ECS hosts
ECS hosts  When people hear about prospecting, they might imagine old forty-niners (miners) with pickaxes hunting for gold, or maybe an agent for the San Francisco 49ers (football team) scouting for new talent. In my lab we do another version, called bio-prospecting – searching for useful substances from natural sources. Bio-prospecting has produced many valuable products, including
When people hear about prospecting, they might imagine old forty-niners (miners) with pickaxes hunting for gold, or maybe an agent for the San Francisco 49ers (football team) scouting for new talent. In my lab we do another version, called bio-prospecting – searching for useful substances from natural sources. Bio-prospecting has produced many valuable products, including 
 A new issue of ECS Transactions (ECST) has just been published from the XXXI National Congress of the Mexican Society of Electrochemistry/9th Meeting of the ECS Mexican Section.
A new issue of ECS Transactions (ECST) has just been published from the XXXI National Congress of the Mexican Society of Electrochemistry/9th Meeting of the ECS Mexican Section.