By: Jackie Flynn, Stanford University
 A battery made with urea, commonly found in fertilizers and mammal urine, could provide a low-cost way of storing energy produced through solar power or other forms of renewable energy for consumption during off hours.
A battery made with urea, commonly found in fertilizers and mammal urine, could provide a low-cost way of storing energy produced through solar power or other forms of renewable energy for consumption during off hours.
Developed by Stanford chemistry Professor Hongjie Dai and doctoral candidate Michael Angell, the battery is nonflammable and contains electrodes made from abundant aluminum and graphite. Its electrolyte’s main ingredient, urea, is already industrially produced by the ton for plant fertilizers.
“So essentially, what you have is a battery made with some of the cheapest and most abundant materials you can find on Earth. And it actually has good performance,” said Dai. “Who would have thought you could take graphite, aluminum, urea, and actually make a battery that can cycle for a pretty long time?”
In 2015, Dai’s lab was the first to make a rechargeable aluminum battery. This system charged in less than a minute and lasted thousands of charge-discharge cycles. The lab collaborated with Taiwan’s Industrial Technology Research Institute (ITRI) to power a motorbike with this older version, earning Dai’s group and ITRI a 2016 R&D 100 Award. However, that version of the battery had one major drawback: it involved an expensive electrolyte.
The newest version includes a urea-based electrolyte and is about 100 times cheaper than the 2015 model, with higher efficiency and a charging time of 45 minutes. It’s the first time urea has been used in a battery. According to Dai, the cost difference between the two batteries is “like night and day.” The team recently reported its work in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.


 Most of today’s batteries are made up of two solid layers, separated by a liquid or gel electrolyte. But some researchers are beginning to move away from that traditional battery in favor of an all-solid-state battery, which some researchers believe could enhance battery energy density and safety. While there are many barriers to overcome when pursing a feasible all-solid-state battery, researchers from MIT believe they are headed in the right direction.
Most of today’s batteries are made up of two solid layers, separated by a liquid or gel electrolyte. But some researchers are beginning to move away from that traditional battery in favor of an all-solid-state battery, which some researchers believe could enhance battery energy density and safety. While there are many barriers to overcome when pursing a feasible all-solid-state battery, researchers from MIT believe they are headed in the right direction. While most car companies are investing research efforts into electric and autonomous vehicles, Uber – the highly popular ride-sharing service – is attempting to stick out in the crowd of auto giants by developing a flying car.
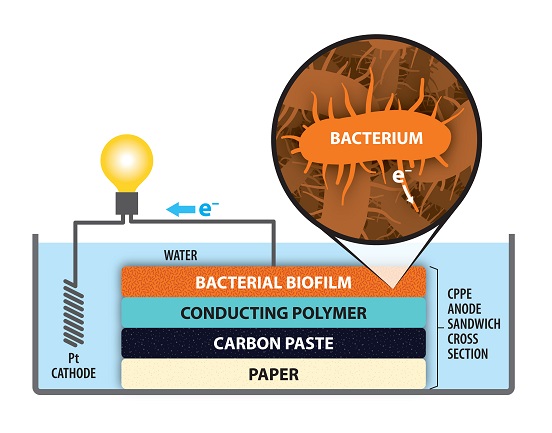
While most car companies are investing research efforts into electric and autonomous vehicles, Uber – the highly popular ride-sharing service – is attempting to stick out in the crowd of auto giants by developing a flying car. In an effort to purify water, researchers from the University at Buffalo are using carbon-dipped paper to make dirty water drinkable.
In an effort to purify water, researchers from the University at Buffalo are using carbon-dipped paper to make dirty water drinkable. New technology that mimics the branches and leaves of a cottonwood tree can generate electricity with the help of the wind.
New technology that mimics the branches and leaves of a cottonwood tree can generate electricity with the help of the wind. When a May 2016 crash
When a May 2016 crash  The
The