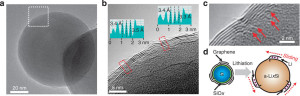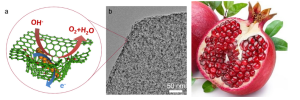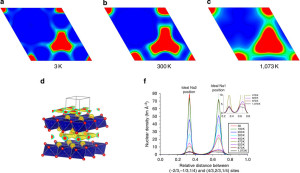
Carbon nanotubes, seamless cylinders of graphene, do not display a total dipole moment. While not zero, the vector-induced moments cancel each other out.
Image: Rice University
Theoretical physicist at both Rice University and institutes in Russia have concluded that the best way to control graphene’s electrical qualities is to flex the material.
Rice University’s Boris Yakobson and his lab are collaborating with Moscow researchers to calculate the electrical properties of nanocones, which should be universal for other forms of graphene.
(PS: You can take a look at some of Yakobson’s past meeting abstracts in the Digital Library.)
This from Rice University:
The researchers discovered it may be possible to access what they call an electronic flexoelectric effect in which the electronic properties of a sheet of graphene can be manipulated simply by twisting it a certain way. The work will be of interest to those considering graphene elements in flexible touchscreens or memories that store bits by controlling electric dipole moments of carbon atoms, the researchers said.
Read the full article here.
“While the dipole moment is zero for flat graphene or cylindrical nanotubes, in between there is a family of cones, actually produced in laboratories, whose dipole moments are significant and scale linearly with cone length,” Yakobson said.
ICYMI: Check out our podcast, “A Word About Nanocarbons,” featuring another Rice University carbon nanotube expert, Dr. Bruce Weisman.
Interested in carbon nanotubes, fullerenes, and nanocarbons? Make sure to check out ECS’s Nanocarbons Division!