 Lithium-air batteries are—in theory—an extremely attractive alternative for affordable, efficient energy storage for electric vehicles. However, as researchers explore this technology, they are met with many critical challenges. If researchers can overcome these challenges, there is a great likelihood that the lithium-air battery will surpass the energy density of today’s lithium-ion battery.
Lithium-air batteries are—in theory—an extremely attractive alternative for affordable, efficient energy storage for electric vehicles. However, as researchers explore this technology, they are met with many critical challenges. If researchers can overcome these challenges, there is a great likelihood that the lithium-air battery will surpass the energy density of today’s lithium-ion battery.
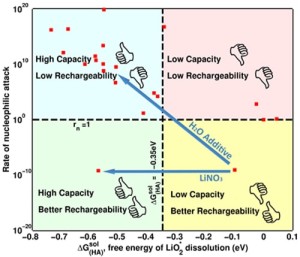
Researchers from Carnegie Mellon University and the University of California, Berkley feel like they may have part of the answer to this critical challenge, which could propel the practicality of the lithium-air battery. The team, which included researchers from Bryan McCloskey and Venkat Viswanathan‘s laboratories, has found a way to both increase the capacity while preserving the recharge ability of the lithium-air battery by blending different types within the battery’s electrolytes.
“The electrolytes used in batteries are just like Gatorade electrolytes,” says Venkat Viswanathan, assistant professor of mechanical engineering at Carnegie Mellon. “Every electrolyte has a solvent and a salt. So if you take Gatorade, the solvent would be water and the salt would be something like sodium chloride, for instance. However, in a lithium air battery, the solvent is dimethoxyethane and the salt is something like lithium hexafluorophosphate.”