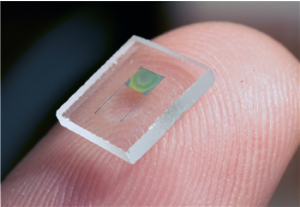
The newly developed black silicon has the potential to simplify the manufacturing of solar cells due to the ability of the material to more efficiently collect light.
Image: Barron Group
One of the roadblocks in developing a new, clean energy infrastructure lies in our ability to manufacture solar cells with ease and efficiency. Now, researchers from Rice University may have developed a way to simplify this process.
In Andrew Barron’s Rice University lab, he and postdoctoral student Yen-Tien Lu are developing black silicon by employing electrodes as catalysts.
The typical solar cell is made from silicon. By swapping that regular silicon for black silicon, solar cells gain a highly textured surface of nanoscale spikes that allows for a more efficient collection of light.
This from Rice University:
Barron said the metal layer used as a top electrode is usually applied last in solar cell manufacturing. The new method known as contact-assisted chemical etching applies the set of thin gold lines that serve as the electrode earlier in the process, which also eliminates the need to remove used catalyst particles.