 An article by Christopher D. Taylor in the latest issue of Interface.
An article by Christopher D. Taylor in the latest issue of Interface.
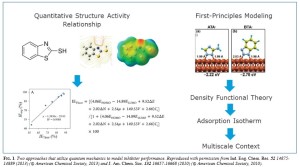
In the late 20th century, computer programs emerged that could solve the fundamental quantum mechanical equations that control the interactions of atoms that give rise to bonding. These tools, first applied to molecules and bulk solid materials, then began to be applied to surfaces and, in the early 21st century, to electrochemical environments. Commercial and open-source programs are now readily available and can be used on both desktop and high-performance computing platforms to solve for the electronic structure of a given configuration of atomic centers (nuclei) and, in so doing, provide the basis for determining a whole host of properties, including electronic and vibrational spectra, electrical moments such as the system dipole, and, most importantly, the energy and forces on the atoms. Other derived properties include the extent to which each atom is charged and bond-orders, although to compute these latter properties one of a variety of methods for dividing up and quantifying the electron density associated with each atom must be selected.
The physics behind these codes is complex, and, challengingly, has no rigorous analytical solution that can be obtained within a finite allotment of time. Thus, the computer programs themselves take advantage of approximations that allow for a feasible solution but, at the same time, constrain the accuracy of the result. Nonetheless, solutions can usually be reliably obtained for model systems representing materials, interfaces, or molecules that do not exceed thousands, and, more realistically, hundreds of atoms. Given that system sizes of hundreds or thousands of atoms amount to no more than the smallest nanoparticle of a substance, the question arises: What can atomistic simulations teach us about corrosion?
Read the rest.