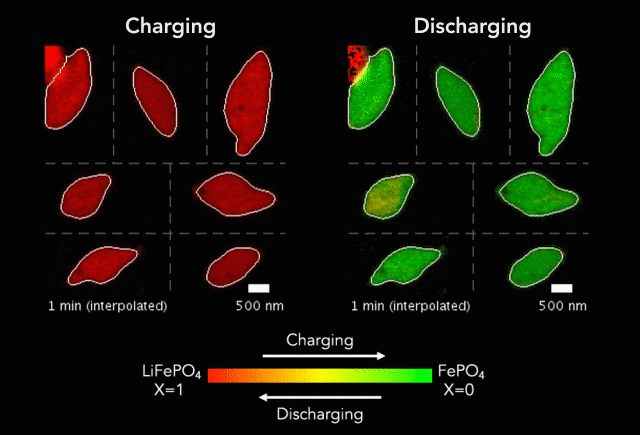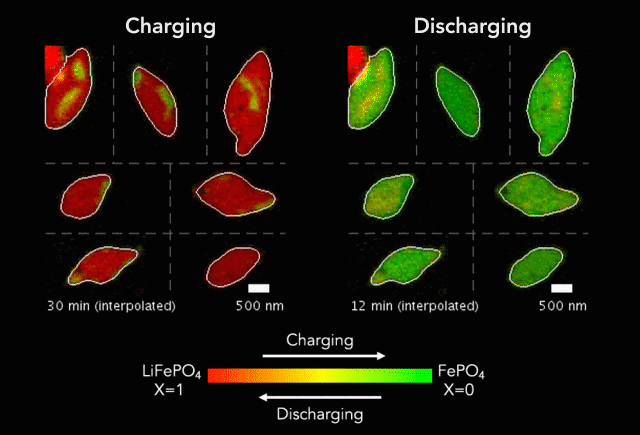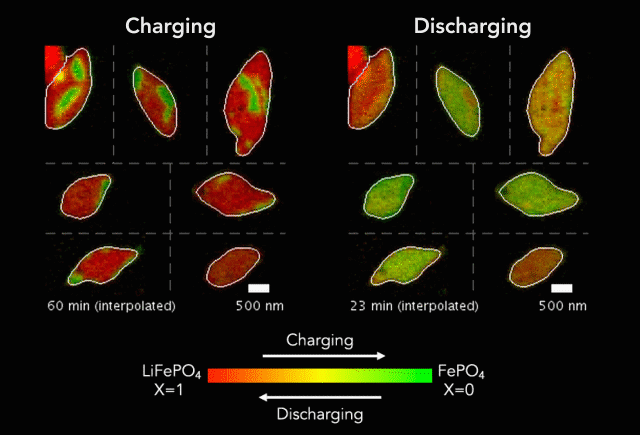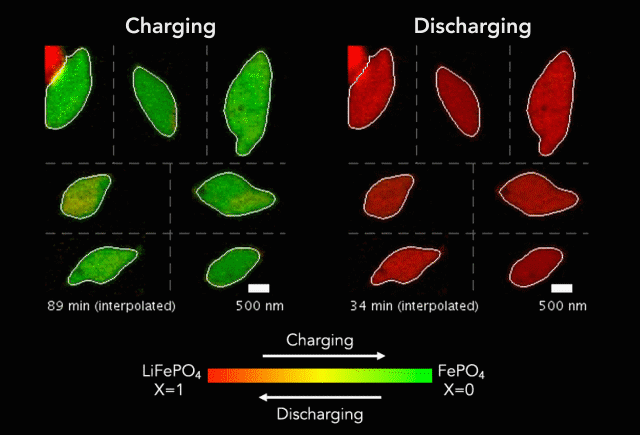
 One of the keys to developing a successful electric vehicle relies on energy storage technology. For an EV to be successful in the marketplace, it must be able to travel longer distances (i.e. over 300 miles on a single charge).
One of the keys to developing a successful electric vehicle relies on energy storage technology. For an EV to be successful in the marketplace, it must be able to travel longer distances (i.e. over 300 miles on a single charge).
A team of researchers from Georgia Institute of Technology, including ECS fellow Meilin Liu, has recently created a nanofiber that they believe could enable the next generation of rechargeable batteries, and with it, EVs. The recently published research describes the team’s development of double perovskite nanofibers that can be used as highly efficient catalysts in fast oxygen evolution reactions. Improvements in this key process could open new possibilities for metal-air batteries.
“Metal-air batteries, such as those that could power electric vehicles in the future, are able to store a lot of energy in a much smaller space than current batteries,” Liu says. “The problem is that the batteries lack a cost-efficient catalyst to improve their efficiency. This new catalyst will improve that process.”


 Twenty-sixteen marked the 25th anniversary of the commercialization of the lithium-ion battery. Since Sony’s move to commercialize the technology in 1991, the clunky electronics that were made possible by the development of the transistor have become sleek, portable devices that play an integral role in our daily lives – thanks in large part to the Li-ion battery.
Twenty-sixteen marked the 25th anniversary of the commercialization of the lithium-ion battery. Since Sony’s move to commercialize the technology in 1991, the clunky electronics that were made possible by the development of the transistor have become sleek, portable devices that play an integral role in our daily lives – thanks in large part to the Li-ion battery.
 Lithium-air batteries are viewed by many as a potential next-generation technology in energy storage. With the highest theoretical energy density of all battery devices, Li-air could revolutionize everything from electric vehicles to large-scale grid storage. However, the relatively young technology has a few barriers to overcome before it can be applied. A new study published in the
Lithium-air batteries are viewed by many as a potential next-generation technology in energy storage. With the highest theoretical energy density of all battery devices, Li-air could revolutionize everything from electric vehicles to large-scale grid storage. However, the relatively young technology has a few barriers to overcome before it can be applied. A new study published in the