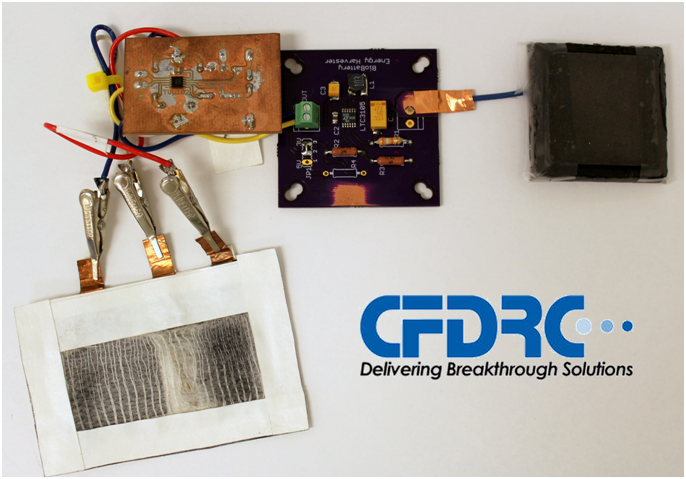
Enzyme-based sensors detect lactate levels in sweat
It may be clammy and inconvenient, but human sweat has at least one positive characteristic – it can give insight to what’s happening inside your body. A new study published in the ECS Journal of Solid State Science and Technology aims to take advantage of sweat’s trove of medical information through the development of a sustainable, wearable sensor to detect lactate levels in your perspiration.
“When the human body undergoes strenuous exercise, there’s a point at which aerobic muscle function becomes anaerobic muscle function,” says Jenny Ulyanova, CFD Research Corporation (CFDRC) researcher and co-author of the paper. “At that point, lactate is produce at a faster rate than it is being consumed. When that happens, knowing what those levels are can be an indicator of potentially problematic conditions like muscle fatigue, stress, and dehydration.”
Utilizing green technology
Using sweat to track changes in the body is not a new concept. While there have been many developments in recent years to sense changes in the concentrations of the components of sweat, no purely biological green technology has been used for these devices. The team of CFDRC researchers, in collaboration with the University of New Mexico, developed an enzyme-based sensor powered by a biofuel cell – providing a safe, renewable power source.
Biofuel cells have become a promising technology in the field of energy storage, but still face many issues related to short active lifetimes, low power densities, and low efficiency levels. However, they have several attractive points, including their ability to use renewable fuels like glucose and implement affordable, renewable catalysts.