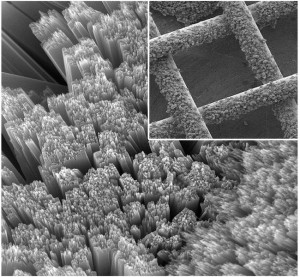
The new solar battery stores power by “breathing” air to decompose and re-form lithium peroxide.
Credit: Yiying Wu/Ohio State University
Is it a solar cell? Is it a rechargeable battery? Well, technically it’s both.
The scientists at Ohio State University have developed the world’s first solar battery that can recharge itself using light and air. The findings from the patent-pending device were published in the October 3, 2014 issue of the journal Nature Communications.
This from Ohio State University:
Key to the innovation is a mesh solar panel, which allows air to enter the battery, and a special process for transferring electrons between the solar panel and the battery electrode. Inside the device, light and oxygen enable different parts of the chemical reactions that charge the battery.
Read the full article here.
The university plans to license the solar battery to industry.
“The state of the art is to use a solar panel to capture the light, and then use a cheap battery to store the energy,” said Yiying Wu, professor of chemistry and biochemistry at Ohio State University. “We’ve integrated both functions into one device. Any time you can do that, you reduce cost.”
The device also tackles the issue of solar energy efficiency by eliminating the loss of electricity that normally occurs when electrons have to travel between a solar cell and an external battery. Where typically only 80 percent of electrons make it from the solar cell into the battery, the new solar battery saves nearly 100 percent of electrons.
Want to know more about what’s going on with solar batteries? Check out the latest research in ECS’s Digital Library and find out what our scientists think the future looks like.
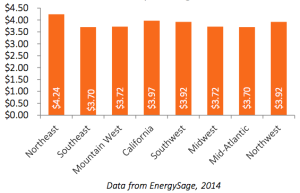 If you haven’t embraced solar energy yet, it may be about time to do so. After all, it is cheaper than grid energy in 42 of the 50 largest cities in the United States.
If you haven’t embraced solar energy yet, it may be about time to do so. After all, it is cheaper than grid energy in 42 of the 50 largest cities in the United States.


