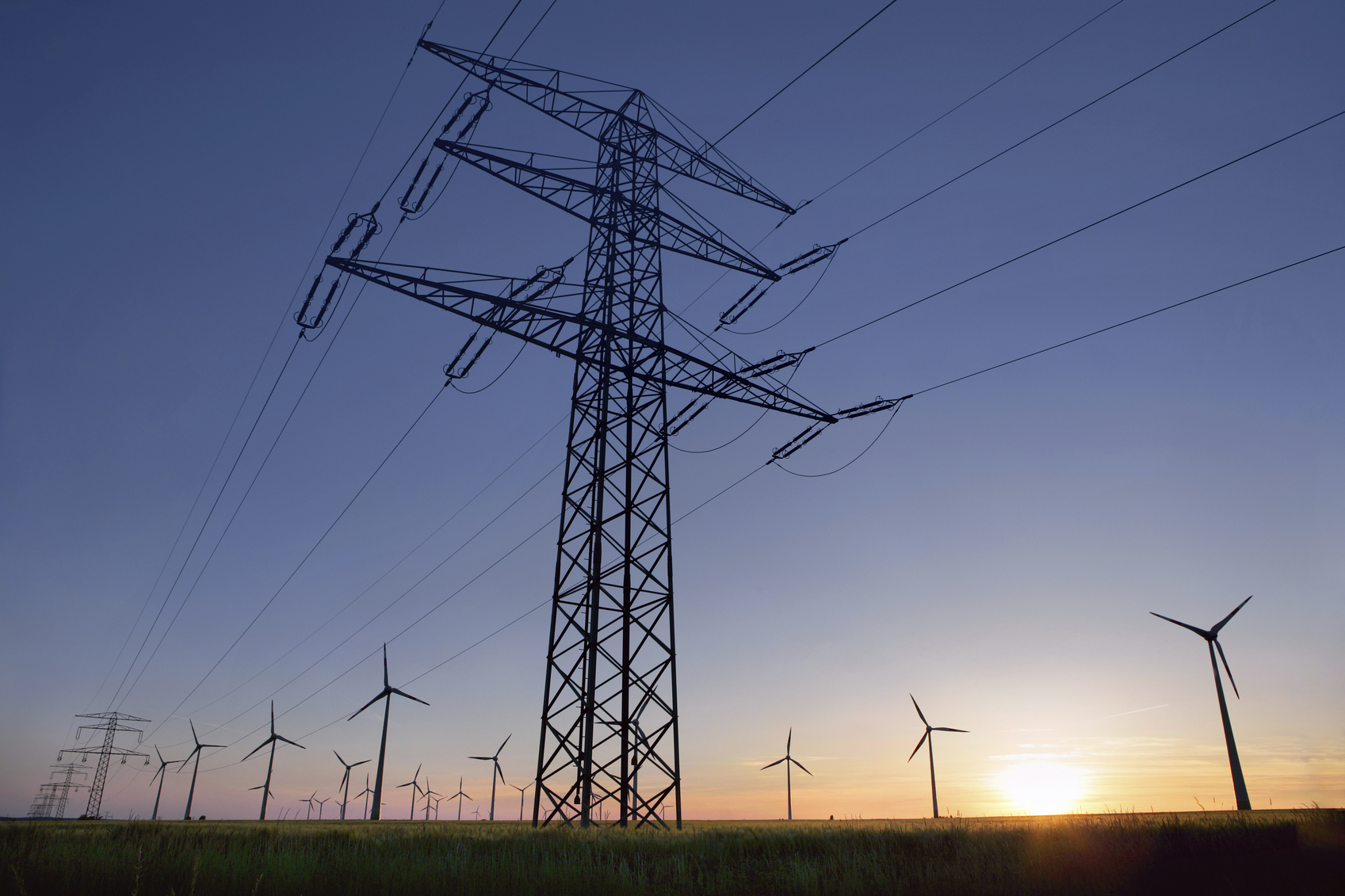
The U.S. Department of Energy (DOE) released a report Wednesday night on electricity markets and grid reliability, stating that the decline in coal and nuclear production has not impacted grid reliability, instead the rise in a diverse energy portfolio has increased the grid’s stability.
The U.S. Department of Energy (DOE) released a report Wednesday night on electricity markets and grid reliability, stating that the decline in coal and nuclear production has not impacted grid reliability, instead the rise in a diverse energy portfolio has increased the grid’s stability.
The study, commissioned by Energy Secretary Rick Perry in April, also states that coal plant closures across the country have been due to market pressure and competition from low-priced natural gas plants, not policy changes that support renewables such as wind and solar.
(MORE: Listen to our interview with former U.S. Energy Secretary and Nobel Laureate Steven Chu.)
“America is also fortunate to have a variety of fuel sources. We need to consider how to use each effectively while recognizing our differences and unique state and regional circumstances,” Perry says in the report’s cover letter. “We must utilize the most effective combination of energy sources with an ‘all of the above’ approach to achieve long-term, reliable American energy security.”
While the report does not state that there is a current concern with grid reliability, it does warn that future problems could arise if coal and nuclear plants continue to close at the current rate. Many environmental advocates cite this as a last-ditch effort for these companies to remain relevant in the energy landscape. However, the report does go on to highlight the role of renewables in developing a diverse energy infrastructure.




 The U.S. Department of Energy recently released a new series of posters illuminating a new generation of sustainable energy and green jobs. The series is reminiscent of the famous imagery created for the Works Progress Administration, only this time, the images depict a renewable energy revolution.
The U.S. Department of Energy recently released a new series of posters illuminating a new generation of sustainable energy and green jobs. The series is reminiscent of the famous imagery created for the Works Progress Administration, only this time, the images depict a renewable energy revolution.