ECS is hosting a series of webinars presented by distinguished speakers this June. Join us! Speakers include Harry Atwater from the California Institute of Technology, Arumugam Manthiram from the University of Texas at Austin, and Paul Kenis from the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign. Topics include batteries, energy, carbon, and more. Considering attending? Learn more about what you can expect to hear about from our presenters! (more…)
ECS is hosting a series of webinars presented by distinguished speakers this June. Join us! Speakers include Harry Atwater from the California Institute of Technology, Arumugam Manthiram from the University of Texas at Austin, and Paul Kenis from the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign. Topics include batteries, energy, carbon, and more. Considering attending? Learn more about what you can expect to hear about from our presenters! (more…)
Neil deGrasse Tyson once said, “Space exploration is a force of nature unto itself that no other force in society can rival.” Unfortunately, there are many factors that stifle human space exploration – one of which is the lack of oxygen.
How people will breathe is a constant concern among space missions. It’s impossible to shuttle oxygen tanks out and the air recycling systems are only about 50 percent efficient when it comes to recovering oxygen from carbon dioxide – but now a new development could mean easy breathing in space.
Research on a discovery from January 2014 is being expanded to develop silver electrocatalysts that may help enable long-term space travel. The original paper, “A selective and efficient electrocatalyst for carbon dioxide reduction,” detailed a development from scientists at the University of Delaware of a silver electrocatalyst that, due to its nanoscale structure, could convert carbon dioxide to carbon monoxide with 92 percent efficiency – freeing the oxygen in the process.
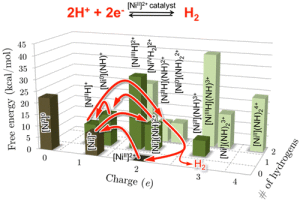
Using a desktop computer, scientists can query the model about the thermodynamic properties needed to create the desired catalysts. They can use those parameters to inform experimentalists in their synthetic work.
Image: Accounts of Chemical Research
We’re one step closer to transitioning renewable energy sources from intermittent to sustainable with this new development from Pacific Northwest National Laboratory.
Scientists are eliminating all of the unnecessary detours when dealing with molecular catalysts by elaborating on a strategy to map the catalytic route. With this strategy, researchers can modify just one part of a catalyst and see how that affects everything – including all the side reactions.
“We now know how catalysts with desired properties will behave in a given circumstance before we ever leave the computer. By working backwards, we can even ask which catalysts are the best performers for a set of conditions. We are on the verge of designing molecular electrocatalysts in silico — or conducting research by means of computer modeling,” said study co-leader, Dr. Simone Raugei.