Joint research from the Universidad Carlos III de Madrid and the Council for Scientific Research reports the development of a new ceramic electrode for lithium-ion batteries that can lead to cheaper, more efficient, and safer conventional batteries.
Joint research from the Universidad Carlos III de Madrid and the Council for Scientific Research reports the development of a new ceramic electrode for lithium-ion batteries that can lead to cheaper, more efficient, and safer conventional batteries.
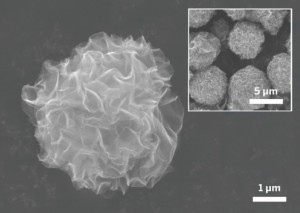
“What we have patented are new ceramic electrodes that are much safer and can work in a wider temperature interval,” says Alejandro Varez, co-author of the research.
To achieve this result, the researchers made ceramic sheets by way of thermoplastic extrusion molds.
“This technique allows making electrodes that are flat or tube-shaped, and these electrodes can be applied to any type of lithium-ion battery,” Varez says.
According to the researchers, the cost of production is low and it could easily be adapted into current lithium-ion battery production, making this an easy technology to move quickly to industrialization.