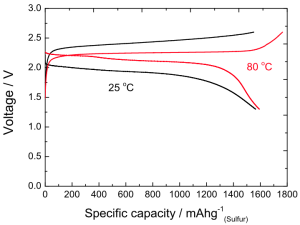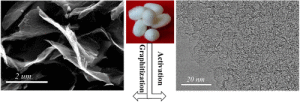
The integration of silk into the lithium-ion battery allowed the battery to work for over 10,000 cycles with only a nine percent loss in stability.
Image: ACS Nano
The words “lithium-ion” and “battery” have become almost synonymous recently. While the li-ion battery is used in a multitude of applications, it still does not have a long life without a recharge.
Now, researchers have developed an environmentally friendly way to boost the performance of the li-ion battery by focusing on a material derived from silk.
In the li-ion battery, carbon is the key component for storage. In most situations, graphite takes that role – but it has limited energy capacity. In order to improve the performance of the li-ion battery, researchers looked to replace graphite with a material developed using a sustainable source.