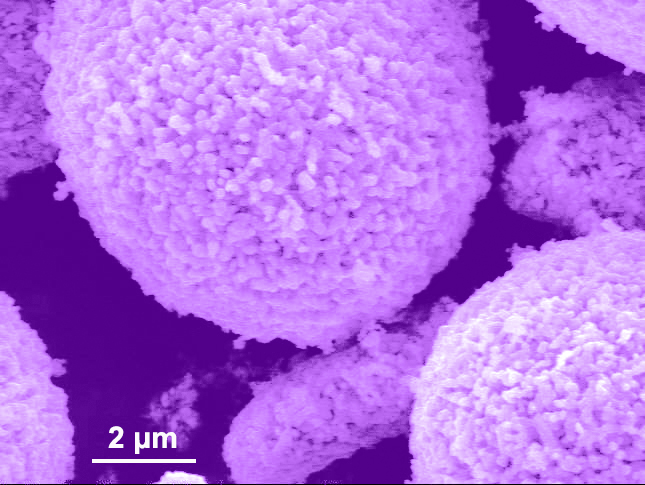
Cathode particles treated with the carbon dioxide-based mixture show oxygen vacancies on the surface.
Image: Laboratory for Energy Storage and Conversion, UC San Diego
An international team of researchers has recently demonstrated a 30 to 40 percent increase in the energy storage capabilities of cathode materials.
The team, led by ECS member and 2016 Charles W. Tobias Young Investigator Award winner, Shirley Meng, has successfully treated lithium-rich cathode particles with a carbon dioxide-based gas mixture. This process introduced oxygen vacancies on the surface of the material, allowing for a huge boost to the amount of energy stored per unit mass and proving that oxygen plays a significant role in battery performance.
This greater understanding and improvement in the science behind the battery materials could accelerate developments in battery performance, specifically in applications such as electric vehicles.
“We’ve uncovered a new mechanism at play in this class of lithium-rich cathode materials,” says Meng, past guest editor of JES Focus Issue on Intercalation Compounds for Rechargeable Batteries. “With this study, we want to open a new pathway to explore more battery materials in which we can control oxygen activity.”