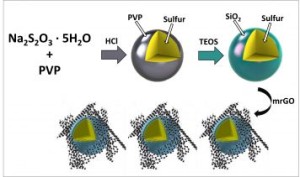
Researchers have investigated a strategy to prevent this “polysulfide shuttling” phenomenon by creating nano-sized sulfur particles, and coating them in silica (SiO2), otherwise known as glass.
Image: Nanoscale
Lithium-sulfur has been a hot topic in battery technology recently. Because of its ability to produce 10 times the amount of energy as a conventional battery, we’ve seen novel innovations such as the all solid state lithium-sulfur battery. Now, the li-sulfur battery is getting a glass coating to further improve its performance.
Researchers at the University of California, Riverside have applied a glass cage-like coating, along with graphene oxide, to the li-sulfur battery. This innovation was developed in order to overcome one of the major issues in commercializing the battery – polysulfides, which cause the battery’s capacity to decrease over its lifetime.
The cathode material traps the polysulfides in a very thin glass cage. Researchers used an organic precursor to construct the trapping barrier.

