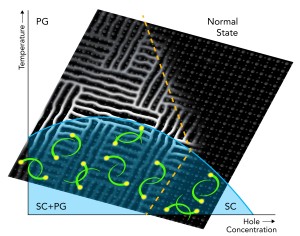
Experiments at SLAC have produced the first direct evidence that the pseudogap competes for electrons with superconductivity over a wide range of temperatures at lower hole concentrations (SC+PG). At lower temperatures and higher hole concentrations, superconductivity wins out.
Credit: SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory
A new study out of the SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory shows the “pseudogap” phase – a mysterious phase of matter – hoards electrons that might otherwise conduct electricity with 100 percent efficiency.
Scientists state that this pseudogap phase competes with high-temperature superconductivity, which robs electrons that would otherwise pair up to carry current though a material.
The results of the study are a culmination of 20 years of research aimed to find out whether the pseudogap helps or hinders superconductivity.
The study shows that the pseudogap is one of the things that stands in the way of getting superconductors to work at higher temperatures for everyday uses – thus making electrical transmission, computing, and other areas less energy efficient.

