 ECS is hosting a series of webinars presented by distinguished speakers this June. Join us! Speakers include Harry Atwater from the California Institute of Technology, Arumugam Manthiram from the University of Texas at Austin, and Paul Kenis from the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign. Topics include batteries, energy, carbon, and more. Considering attending? Learn more about what you can expect to hear about from our presenters! (more…)
ECS is hosting a series of webinars presented by distinguished speakers this June. Join us! Speakers include Harry Atwater from the California Institute of Technology, Arumugam Manthiram from the University of Texas at Austin, and Paul Kenis from the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign. Topics include batteries, energy, carbon, and more. Considering attending? Learn more about what you can expect to hear about from our presenters! (more…)
Call for Papers: Gallium Oxide Based Materials and Devices II
Posted on December 17, 2019 by Frances Chaves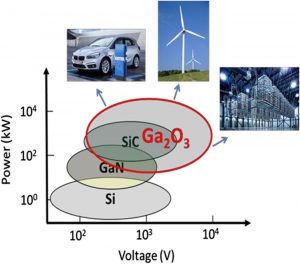 Accepting Submissions: December 26, 2019 – March 25, 2020
Accepting Submissions: December 26, 2019 – March 25, 2020
Submit your manuscripts to the ECS Journal of Solid State Science and Technology Focus Issue on Gallium Oxide Based Materials and Devices II.
About the focus issue
This issue of the ECS Journal of Solid State Science and Technology is the second in a series that aims to cover the growth, characterization, processing and device applications of Ga2O3. GaN and SiC based wide bandgap device technologies have matured and become limited by fundamental material properties. A new class of oxide wide band gap materials are emerging (gallium oxide and aluminum gallium oxide) that offer potentially improved figure of merit over GaN and SiC for power devices. The availability of Ga2O3 single crystals and epitaxial films with large area and excellent quality has led to renewed interest in this ultra-wide bandgap semiconductor for solar-blind photodetectors, sensors, and power electronics. (more…)
By: Joshua M. Pearce, Michigan Technological University
 Falling costs for solar power have led to an explosive growth in residential, commercial and utility-scale solar use over the past decade. The levelized cost of solar electricity using imported solar panels – that is, the solar electricity cost measured over the life of the panels – has dropped in cost so much that it is lower than electricity from competing sources like coal in most of America.
Falling costs for solar power have led to an explosive growth in residential, commercial and utility-scale solar use over the past decade. The levelized cost of solar electricity using imported solar panels – that is, the solar electricity cost measured over the life of the panels – has dropped in cost so much that it is lower than electricity from competing sources like coal in most of America.
However, the Trump administration on Jan. 22 announced a 30 percent tariff on solar panel imports into the U.S. This decision is expected to slow both the deployment of large-scale solar farms in the United States and the rate of American solar job growth (which is 12 times faster than the rest of the economy). The tariff increases the cost of solar panels by about 10 to 15 cents per watt. That could reduce utility-scale solar installations, which have come in under $1 per watt, by about 11 percent.
The tariffs may lead China and other countries to appeal the move with the World Trade Organization. But could innovations in solar power compensate for tariffs on panels?
In my research, I have found that one solar technology – previously largely ignored because of low-cost photovoltaics, or PV, panels – could make a comeback: the humble mirror, or booster reflector, as it is known in the technical literature.
Researchers have found a way to get electrons to travel much farther than was previously thought possible in materials for organic solar cells. This advance could make these solar cells much more useful than inorganic alternatives.
“For years, people had treated the poor conductivity of organics as an unavoidable fact, and this shows that that’s not always the case,” says research leader Stephen Forrest, professor of engineering at University of Michigan.
To Generate More Solar Power, Put This Material on Glass
Posted on October 25, 2017 by Amanda StallerTransparent solar materials on windows could gather as much energy as bulkier rooftop solar units, say researchers.
The authors of a new paper argue that widespread use of such highly transparent solar applications, together with the rooftop units, could nearly meet US electricity demand and drastically reduce the use of fossil fuels.
“Highly transparent solar cells represent the wave of the future for new solar applications,” says Richard Lunt, an associate professor of chemical engineering and materials science at Michigan State University. “We analyzed their potential and show that by harvesting only invisible light, these devices can provide a similar electricity-generation potential as rooftop solar while providing additional functionality to enhance the efficiency of buildings, automobiles, and mobile electronics.”
Using unique design and building methods, researchers have created a prototype for an ultra-thin, curving concrete roof that will also generate solar power.
The self-supporting, doubly curved shell roof has multiple layers: the heating and cooling coils and the insulation are installed over the inner concrete layer. A second, exterior layer of the concrete sandwich structure encloses the roof, onto which builders install thin-film photovoltaic cells.
Philippe Block, a professor of architecture and structures at ETH Zurich, and Arno Schlüter, a professor of architecture and building systems, led the team. They want to put the new lightweight construction to the test and combine it with intelligent and adaptive building systems.
Boost for Solar Cells Also Makes Self-Driving Cars Safer
Posted on October 6, 2017 by Amanda Staller Engineers working to make solar cells more cost effective ended up finding a method for making sonar-like collision avoidance systems in self-driving cars.
Engineers working to make solar cells more cost effective ended up finding a method for making sonar-like collision avoidance systems in self-driving cars.
The twin discoveries started, the researchers say, when they began looking for a solution to a well-known problem in the world of solar cells.
Solar cells capture photons from sunlight in order to convert them into electricity. The thicker the layer of silicon in the cell, the more light it can absorb, and the more electricity it can ultimately produce. But the sheer expense of silicon has become a barrier to solar cost-effectiveness.
So the engineers figured out how to create a very thin layer of silicon that could absorb as many photons as a much thicker layer of the costly material. Specifically, rather than laying the silicon flat, they nanotextured the surface of the silicon in a way that created more opportunities for light particles to be absorbed.
Their technique increased photon absorption rates for the nanotextured solar cells compared to traditional thin silicon cells, making more cost-effective use of the material.
How Solar Power Can Protect the US Military From Threats to the Electric Grid
Posted on September 14, 2017 by Amanda StallerBy: Joshua M. Pearce, Michigan Technology University
 As the U.S. military increases its use of drones in surveillance and combat overseas, the danger posed by a threat back at home grows. Many drone flights are piloted by soldiers located in the U.S., even when the drones are flying over Yemen or Iraq or Syria. Those pilots and their control systems depend on the American electricity grid – large, complex, interconnected and very vulnerable to attack.
As the U.S. military increases its use of drones in surveillance and combat overseas, the danger posed by a threat back at home grows. Many drone flights are piloted by soldiers located in the U.S., even when the drones are flying over Yemen or Iraq or Syria. Those pilots and their control systems depend on the American electricity grid – large, complex, interconnected and very vulnerable to attack.
Without electricity from civilian power plants, the most advanced military in world history could be crippled. The U.S. Department of Energy has begged for new authority to defend against weaknesses in the grid in a nearly 500-page comprehensive study issued in January 2017 warning that it’s only a matter of time before the grid fails, due to disaster or attack. A new study by a team I led reveals the three ways American military bases’ electrical power sources are threatened, and shows how the U.S. military could take advantage of solar power to significantly improve national security.
A triple threat
The first threat to the electricity grid comes from nature. Severe weather disasters resulting in power outages cause between US$25 billion and $70 billion in the U.S. each year – and that’s average years, not those including increasingly frequent major storms, like Hurricanes Harvey and Irma.
The second type of threat is from traditional acts of crime or terrorism, such as bombing or sabotage. For example, a 2013 sniper attack on a Pacific Gas and Electric substation in California disabled 17 transformers supplying power to Silicon Valley. In what the head of the Federal Energy Regulatory Commission called “the most significant incident of domestic terrorism involving the grid that has ever occurred,” the attacker – who may have been an insider – fired about 100 rounds of .30-caliber rifle ammunition into the radiators of 17 electricity transformers over the course of 19 minutes. The electronics overheated and shut down. Fortunately, power company engineers managed to keep the lights on in Silicon Valley by routing power from other sources.
 The U.S. Department of Energy (DOE) released a report Wednesday night on electricity markets and grid reliability, stating that the decline in coal and nuclear production has not impacted grid reliability, instead the rise in a diverse energy portfolio has increased the grid’s stability.
The U.S. Department of Energy (DOE) released a report Wednesday night on electricity markets and grid reliability, stating that the decline in coal and nuclear production has not impacted grid reliability, instead the rise in a diverse energy portfolio has increased the grid’s stability.
The study, commissioned by Energy Secretary Rick Perry in April, also states that coal plant closures across the country have been due to market pressure and competition from low-priced natural gas plants, not policy changes that support renewables such as wind and solar.
(MORE: Listen to our interview with former U.S. Energy Secretary and Nobel Laureate Steven Chu.)
“America is also fortunate to have a variety of fuel sources. We need to consider how to use each effectively while recognizing our differences and unique state and regional circumstances,” Perry says in the report’s cover letter. “We must utilize the most effective combination of energy sources with an ‘all of the above’ approach to achieve long-term, reliable American energy security.”
While the report does not state that there is a current concern with grid reliability, it does warn that future problems could arise if coal and nuclear plants continue to close at the current rate. Many environmental advocates cite this as a last-ditch effort for these companies to remain relevant in the energy landscape. However, the report does go on to highlight the role of renewables in developing a diverse energy infrastructure.
 Researchers have created a concentrating photovoltaic (CPV) system with embedded microtracking that is capable of producing 50 percent more energy per day than the standard silicon solar cells.
Researchers have created a concentrating photovoltaic (CPV) system with embedded microtracking that is capable of producing 50 percent more energy per day than the standard silicon solar cells.
“Solar cells used to be expensive, but now they’re getting really cheap,” says Chris Giebink, an assistant professor of electrical engineering at Penn State.
“As a result, the solar cell is no longer the dominant cost of the energy it produces. The majority of the cost increasingly lies in everything else—the inverter, installation labor, permitting fees, etc.—all the stuff we used to neglect,” he says.
This changing economic landscape has put a premium on high efficiency. In contrast to silicon solar panels, which currently dominate the market at 15 to 20 percent efficiency, concentrating photovoltaics focus sunlight onto smaller, but much more efficient solar cells like those used on satellites, to enable overall efficiencies of 35 to 40 percent.


